Moawia Atrash/picture alliance via Getty Images
Sandra Joireman, University of Richmond
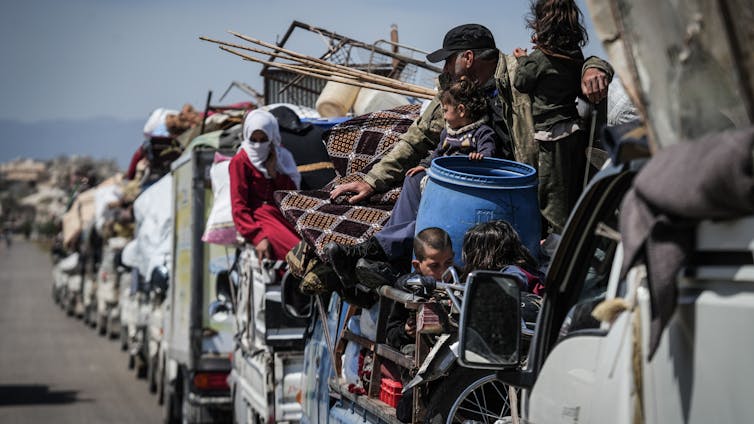
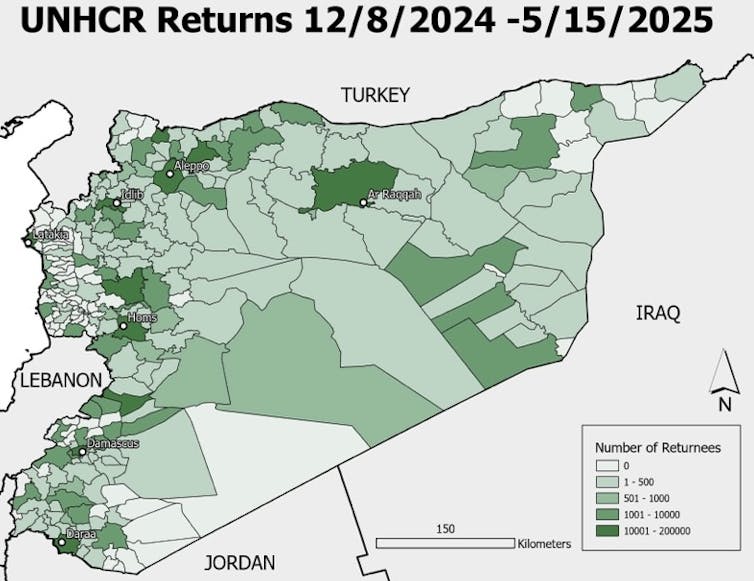
Close to 1.5 million Syrian refugees have voluntarily returned to their home country over the past year.
That extraordinary figure represents nearly one-quarter of all Syrians who fled fighting during the 13-year civil war to live abroad. It is also a strikingly fast pace for a country where insecurity persists across broad regions.
The scale and speed of these returns since the overthrow of Bashar Assad’s brutal regime on Dec. 8, 2024, raise important questions: Why are so many Syrians going back, and will these returns last? Moreover, what conditions are they returning to?
As an expert in property rights and post-conflict return migration, I have monitored the massive surge in refugee returns to Syria throughout 2024. While a combination of push-and-pull factors have driven the trend, the widespread destruction of property during the brutal civil war poses an ongoing obstacle to resettlement.
Where are Syria’s refugees?
By the time a rebel coalition led by Sunni Islamist organization Hayat Tahrir al-Sham overthrew the Assad government, Syria’s civil war had been going on for more than a decade. What began in 2011 as part of the Arab Spring protests quickly escalated into one of the most destructive conflicts of the 21st century.
Millions of Syrians were displaced internally, and about 6 million sought refuge abroad. The majority went to neighboring countries, including Turkey, Jordan and Lebanon, but a little over a million sought refuge in Europe.
Now, European countries are struggling to determine how they should respond to the changed environment in Syria. Germany and Austria have put a hold on processing asylum applications from Syrians. The international legal principle of non-refoulement prohibits states from returning refugees to unsafe environments where they would face persecution and violence.
But people can choose to return home on their own. And the fall of Assad altered refugees’ perceptions of safety and possibility.
Indeed, the U.N. refugee agency surveys conducted in January 2025 across Jordan, Lebanon, Iraq and Egypt found that 80% of Syrian refugees hoped to return home – up sharply from 57% the previous year. But hope and reality are not always aligned, and the factors motivating return are far more complex than the change in political authority.

Why are people returning?
In most post-conflict settings, voluntary return begins only after security improves, schools reopen, basic infrastructure is restored and housing reconstruction is underway. Even then, people often return to their country but not their original communities, especially when local political control has shifted or reconstruction remains incomplete.
In present-day Syria, violence continues in several regions, governance is fragmented, and sectarian conflicts persist. Yet refugees are returning anyway.
A major factor is the deteriorating conditions in neighboring host countries. Most of those who came back to Syria in the early months after Assad’s fall came from neighboring states that have hosted large refugee populations for more than a decade and are now struggling with economic crises, political tensions and declining aid.
In Turkey, for example, Syrians have faced increasing deportations and growing structural barriers to integration, such as temporary status without the possibility of naturalization and strict local registration policies.
In Lebanon, meanwhile, recent violence and a steep drop in international assistance have left Syrian refugees unable to secure food, education and health care.
And in Jordan, international reductions in humanitarian support have made daily life more precarious for refugees.
In other words, many Syrians are not returning because their homeland has become safer, but because the places where they sought refuge have become more difficult.
We do not have data on the religious or ethnic makeup of returnees. But patterns from other post-conflict settings suggest that returnees are usually from the majority community aligned with the new dominant political actors. After the war in Kosovo, for instance, ethnic Albanians returned quickly, while Serb and Roma minorities returned in much smaller numbers due to insecurity and threats of reprisals.
If Syria follows this trajectory, Sunni Muslims may return in higher numbers, as the country’s president, Ahmed al-Sharaa, led the Sunni rebel coalition that overthrew Assad.
Syrian minority groups, including Alawites, Christians, Druze and Kurds, may avoid returning altogether. Violent incidents targeting minority communities have underscored ongoing instability. Recent attacks on the Alawite population have triggered new waves of displacement into Lebanon, while conflicts between Druze militias and the government in Sweida, in southern Syria, have led to more displacement within the country. These episodes illustrate that while pockets of the country may feel safe to some, instability persists.


Ercin Erturk/Anadolu via Getty Images
Barriers to returns
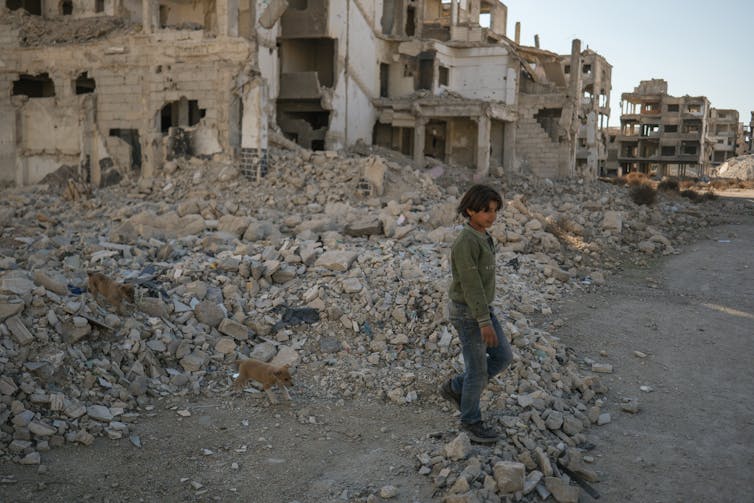
One of the most significant obstacles facing refugees who wish to return is the condition of their homes and the status of their property rights.
The civil war caused widespread destruction of housing, businesses and public buildings.
Land administration systems, including registry offices and records, were damaged or destroyed. This matters because refugees’ return requires more than physical safety; people need somewhere to live and proof that the home they return to is legally theirs.
Analysis by the conflict-monitoring group ACLED of more than 140,000 qualitative reports of violent incidents between 2014 and 2025 shows that property-related destruction was more concentrated in inland provinces than in the coastal regions, with cities such as Aleppo, Idlib and Homs sustaining some of the heaviest damage.
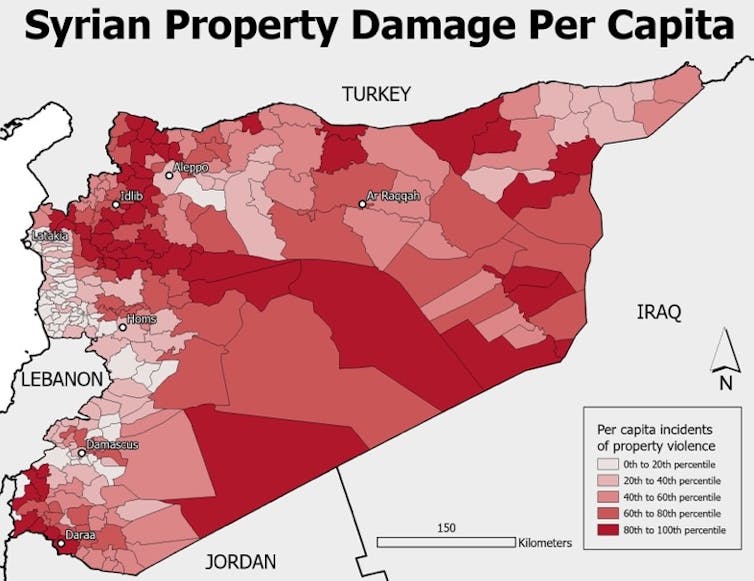

This has major implications for where return is feasible and where it will stall. With documentation lost, homes reoccupied and records destroyed, many Syrians risk returning to legal uncertainty or direct – and sometimes violent – conflict over land and housing.
Post-civil war reconstruction will require not only the rebuilding of physical infrastructure but also the restoration of land governance, including mechanisms for property verification, dispute resolution and compensation. Without all this, refugee returns will likely slow as people confront uncertainty about whether they can reclaim their homes.
Shaping Syria
Whether the wave of returns throughout 2025 continues or proves to be a temporary surge will depend on three main criteria: the security situation in Syria, reconstruction of houses and land administration systems, and the policies of the countries hosting Syrian refugees.
But ultimately, a year after the civil war ended, Syrians are returning because of a mixture of hope and hardship: hope that the fall of the Assad government has opened a path home, and hardship driven by declining support and safety in neighboring states.
Whether these returns will be safe, voluntary and sustainable are critical questions that will shape Syria’s recovery for years to come.![]()
![]()
Sandra Joireman, Weinstein Chair of International Studies, Professor of Political Science, University of Richmond
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.