Stefan Wolff, University of Birmingham and Tetyana Malyarenko, National University Odesa Law Academy
Ukraine is under unprecedented pressure, not only on the battlefield but also on the domestic and diplomatic fronts.
Each of these challenges on their own would be difficult to handle for any government. But together – and given there is no obvious solution to any of the problems the country is facing – they create a near-perfect storm.
It’s a storm that threatens to bring down Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelensky’s government and deal a severe blow to Ukraine’s western allies.
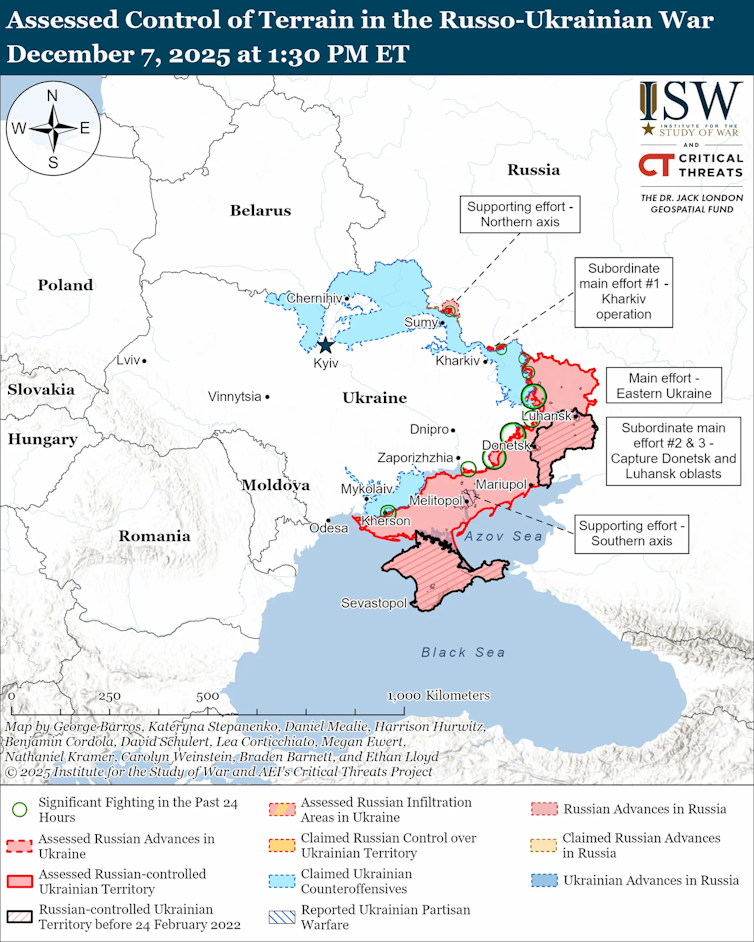
On the frontlines in eastern Donbas, Ukraine has continued to lose territory since Russia’s summer offensive began in May 2025. The ground lost has been small in terms of area but significant in terms of the human and material cost.
Between them, Russia and Ukraine have suffered around 2 million casualties over the course of the war.
Perhaps more importantly, the people of Ukraine have endured months and months during which the best news has been that its troops were still holding out despite relentless Russian assaults. This relentless negativity has undermined morale among troops and civilians alike.
As a consequence, recruitment of new soldiers cannot keep pace with losses incurred on the frontlines – both in terms of casualties and desertions.
Moreover, potential conscripts to the Ukrainian army increasingly resort to violence to avoid being drafted into the military. A new recruitment drive, announced by the Ukrainian commander-in-chief, Oleksandr Syrsky, will increase the potential for further unrest.
Russia’s air campaign against Ukraine’s critical infrastructure continues unabated, further damaging what is left of the vital energy grid and leaving millions of families facing lengthy daily blackouts.
The country’s air defence systems are increasingly overwhelmed by nightly Russian attacks, which are penetrating hitherto safe areas such as the capital and key population centres in south and west. It’s a grim outlook for Ukraine’s civilian population who are now heading into the war’s fourth winter. A ceasefire, let alone a viable peace agreement, remains a very distant prospect.
The political turmoil that has engulfed Zelensky and his government adds to the sense of a potentially catastrophic downward spiral. There have been corruption scandals before, but none has come as close to the president himself.
The amounts allegedly involved in the latest bribery scandal – around US$100m (£75 million) – are eye-watering at a time of national emergency. But it is also the callousness of Ukraine’s elites apparently enriching themselves that adds insult to injury.
The latest scandal has also opened a potential Pandora’s box of vicious recriminations. As more and more members of Zelensky’s inner circle are engulfed in corruption allegations, more details of how different parts of his administration benefited from various schemes or simply turned a blind eye are likely to emerge.
This has damaged Zelensky’s own standing with his citizens and allies. What has helped him survive are both his track record as a war leader so far and the lack of alternatives.
Without a clear pathway towards a smooth transition to a new leadership in Ukraine, the mutual dependency between Zelensky and his European allies has grown.
Whose side is the US on anyway?
The US under Donald Trump is no longer, and perhaps never has been, a dependable ally for Ukraine. What is worse, however, is that America has also ceased to be a dependable ally for Europe.
America’s new national security strategy, published last week, has exploded into this already precarious situation and has sent shockwaves across the whole of Europe. It casts the European Union as more of a threat to US interests than Russia.
It also threatens open interference in the domestic affairs of its erstwhile European allies. And crucially for Kyiv, it outlines a trajectory towards American disengagement from European security.
This adds to Ukraine’s problems – not only because Washington cannot be seen as an honest broker in negotiations with Moscow. It also decreases the value of any western security guarantees. In the absence of a US backstop, the primarily European coalition of the willing lacks the capacity, for now, to establish credible deterrence against future Russian adventurism.

Institute for the Study of War
Efforts by the coalition of the willing cannot hide the fact that a fractured European Union whose key member states, like France and Germany, have fragile governments that are challenged by openly pro-Trump and pro-Putin populists, is unlikely to step quickly into the assurance gap left by the US. The twin challenge of investing in their own defensive capabilities while keeping Ukraine in the fight against Russia to buy the essential time needed to do so creates a profound dilemma.
Can Europe and Ukraine go it alone?
Without the US, Ukraine’s allies simply do not have the resources to enable Ukraine to even improve its negotiation position, let alone to win this war. In a worst-case scenario, all they may be able to accomplish is delaying a Ukrainian defeat.
But this may still be better than a peace deal that would require enormous resources for Ukraine’s reconstruction, while giving Russia an opportunity to regroup, rebuild and rearm for Putin’s next steps towards an even greater Russian sphere of influence in Europe.
At this moment, neither Zelensky nor his European allies can therefore have any interest in a peace deal negotiated between Trump and Putin.
A resignation by Zelensky or his government is unlikely to improve the situation. On the contrary, it is likely to add to Ukraine’s problems. Any new government would be subject to the most intense pressure to accept an imposed deal that Trump and Putin may be conspiring to strike.
Eventually, this war will end, and it will almost certainly require painful concessions from Ukraine. For Europe, the time until then needs to be used to develop a credible plan for stabilising Ukraine, deterring Russia and learning to live and survive without the transatlantic alliance.
The challenge for Europe is to do all three things simultaneously. The danger for Zelensky is that – for Europe – deterring Russia and appeasing the US become existential priorities in themselves and that he and Ukraine could end up as bargaining chips in a bigger game.![]()
![]()
Stefan Wolff, Professor of International Security, University of Birmingham and Tetyana Malyarenko, Professor of International Security, Jean Monnet Professor of European Security, National University Odesa Law Academy
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.