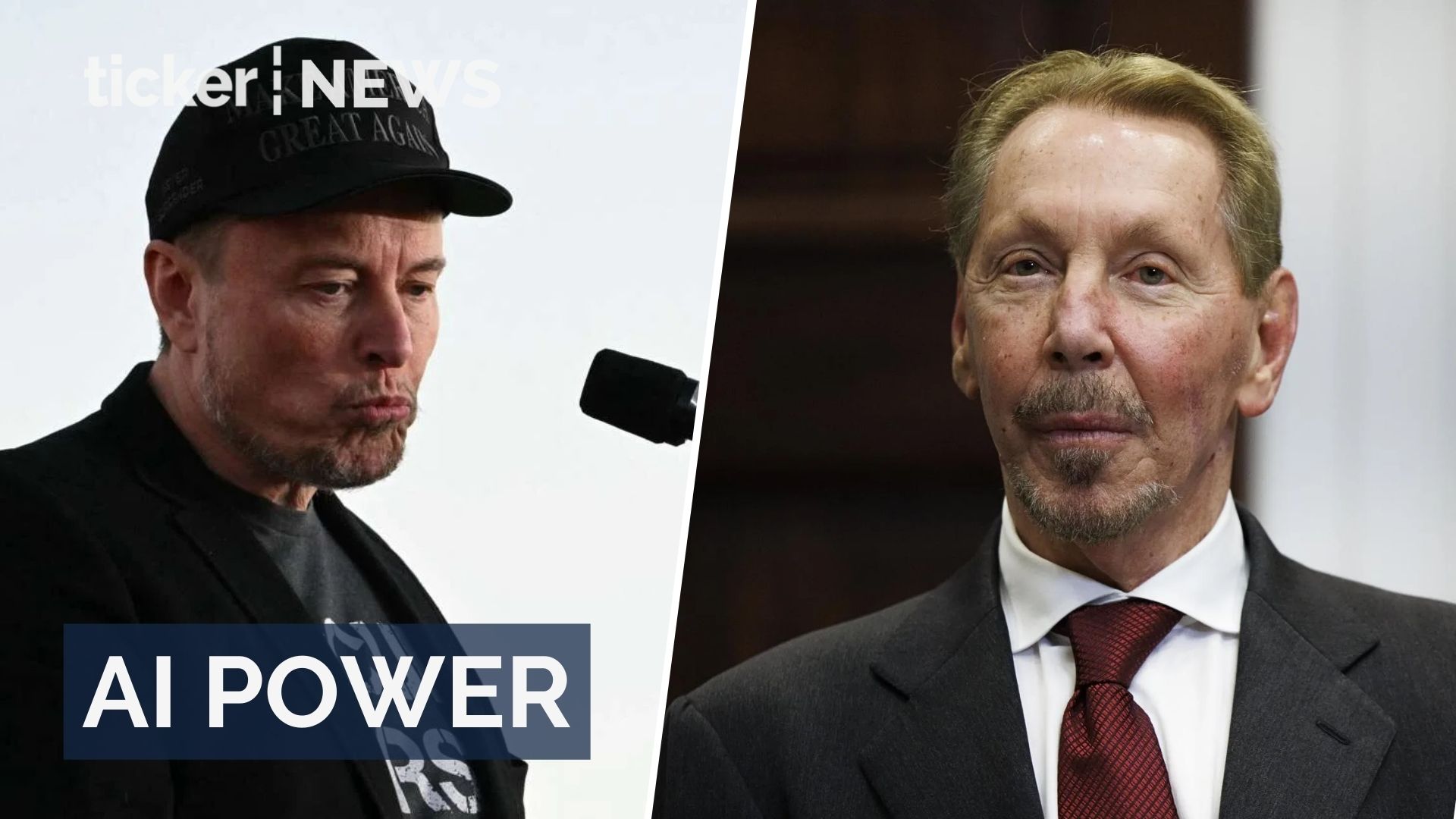
Just for a moment this week, Larry Ellison, co-founder of US cloud computing company Oracle, became the world’s richest person.
The octogenarian tech titan briefly overtook Elon Musk after Oracle’s share price rocketed 43% in a day, adding about US$100 billion (A$150 billion) to his wealth.
The reason? Oracle inked a deal to provide artificial intelligence (AI) giant OpenAI with US$300 billion (A$450 billion) in computing power over five years.
While Ellison’s moment in the spotlight was fleeting, it also illuminated something far more significant: AI has created extraordinary levels of concentration in global financial markets.
This raises an uncomfortable question not only for seasoned investors – but also for everyday Australians who hold shares in AI companies via their superannuation. Just how exposed are even our supposedly “safe”, “diversified” investments to the AI boom?
The man who built the internet’s memory
As billionaires go, Ellison isn’t as much of a household name as Tesla and SpaceX’s Musk or Amazon’s Jeff Bezos. But he’s been building wealth from enterprise technology for nearly five decades.
Ellison co-founded Oracle in 1977, transforming it into one of the world’s largest database software companies. For decades, Oracle provided the unglamorous but essential plumbing that kept many corporate systems running.
The AI revolution changed everything. Oracle’s cloud computing infrastructure, which helps companies store and process vast amounts of data, became critical infrastructure for the AI boom.
Every time a company wants to train large language models or run machine learning algorithms, they need huge amounts of computing power and data storage. That’s precisely where Oracle excels.
When Oracle reported stronger-than-expected quarterly earnings this week, driven largely by soaring AI demand, its share price spiked.
That response wasn’t just about Oracle’s business fundamentals. It was about the entire AI ecosystem that has been reshaping global markets since ChatGPT’s public debut in late 2022.
The great AI concentration
Oracle’s story is part of a much larger phenomenon reshaping global markets. The so-called “Magnificent Seven” tech stocks – Apple, Microsoft, Alphabet, Amazon, Meta, Tesla and Nvidia – now control an unprecedented share of major stock indices.
Year-to-date in 2025, these seven companies have come to represent approximately 39% of the US S&P500’s total value. For the tech-heavy NASDAQ100, the figure is a whopping 74%.
This means if you invest in an exchange-traded fund that tracks the S&P500 index, often considered the gold standard of diversified investing, you’re making an increasingly concentrated bet on AI, whether you realise it or not.
Are we in an AI ‘bubble’?
This level of concentration has not been seen since the late 1990s. Back then, investors were swept up in “dot-com mania”, driving technology stock prices to unsustainable levels.
When reality finally hit in March 2000, the tech-heavy Nasdaq crashed 77% over two years, wiping out trillions in wealth.
Today’s AI concentration raises some similar red flags. Nvidia, which controls an estimated 90% of the AI chip market, currently trades at more than 30 times expected earnings. This is expensive for any stock, let alone one carrying the hopes of an entire technological revolution.
Yet, unlike the dot-com era, today’s AI leaders are profitable companies with real revenue streams. Microsoft, Apple and Google aren’t cash-burning startups. They are established giants, using AI to enhance existing businesses while generating substantial profits.
This makes the current situation more complicated than a simple “bubble” comparison. The academic literature on market bubbles suggests genuine technological innovation often coincides with speculative excess.
The question isn’t whether AI is transformative; it clearly is. Rather, the question is whether current valuations reflect realistic expectations about future profitability.
Hidden exposure for many Australians
For Australians, the AI concentration problem hits remarkably close to home through our superannuation system.
Many balanced super fund options include substantial allocations to international shares, typically 20–30% of their portfolios.
When your super fund buys international shares, it’s often getting heavy exposure to those same AI giants dominating US markets.
The concentration risk extends beyond direct investments in tech companies. Australian mining companies, such as BHP and Fortescue, have become indirect AI players because their copper, lithium and rare earth minerals are essential for AI infrastructure.
Even diversifying away from technology doesn’t fully escape AI-related risks. Research on portfolio concentration shows when major indices become dominated by a few large stocks, the benefits of diversification diminish significantly.
If AI stocks experience a significant correction or crash, it could disproportionately impact Australians’ retirement nest eggs.
A reality check
This situation represents what’s called “systemic concentration risk”. This is a specific form of systemic risk where supposedly diversified investments become correlated through common underlying factors or exposures.
It’s reminiscent of the 2008 financial crisis, when seemingly separate housing markets across different regions all collapsed simultaneously. That was because they were all exposed to subprime mortgages with high risk of default.
This does not mean anyone should panic. But regulators, super fund trustees and individual investors should all be aware of these risks. Diversification only works if returns come from a broad range of companies and industries.![]()
![]()
Angel Zhong, Professor of Finance, RMIT University and Jason Tian, Senior Lecturer, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.